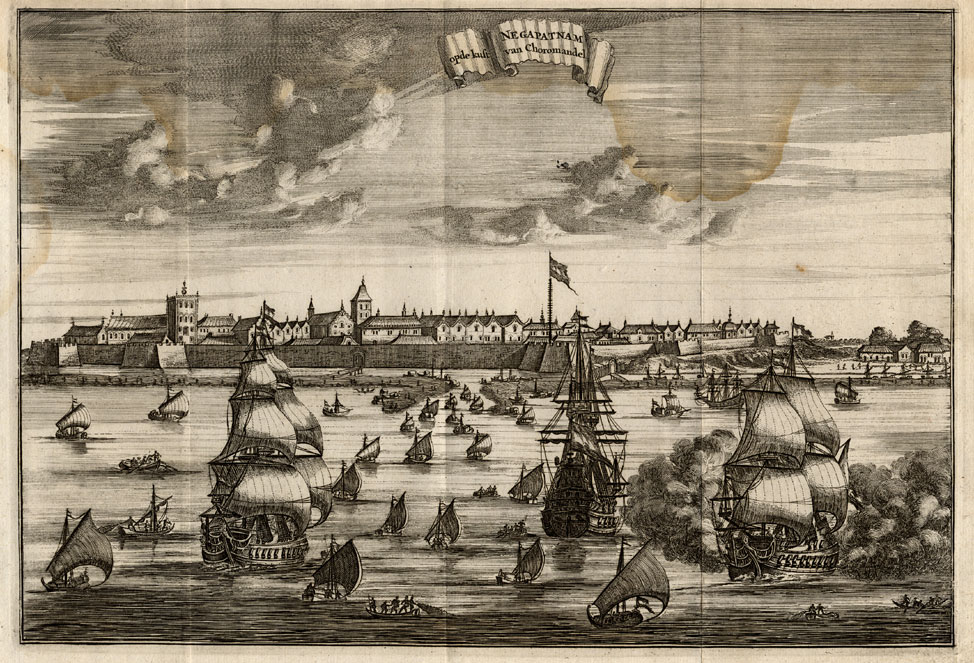
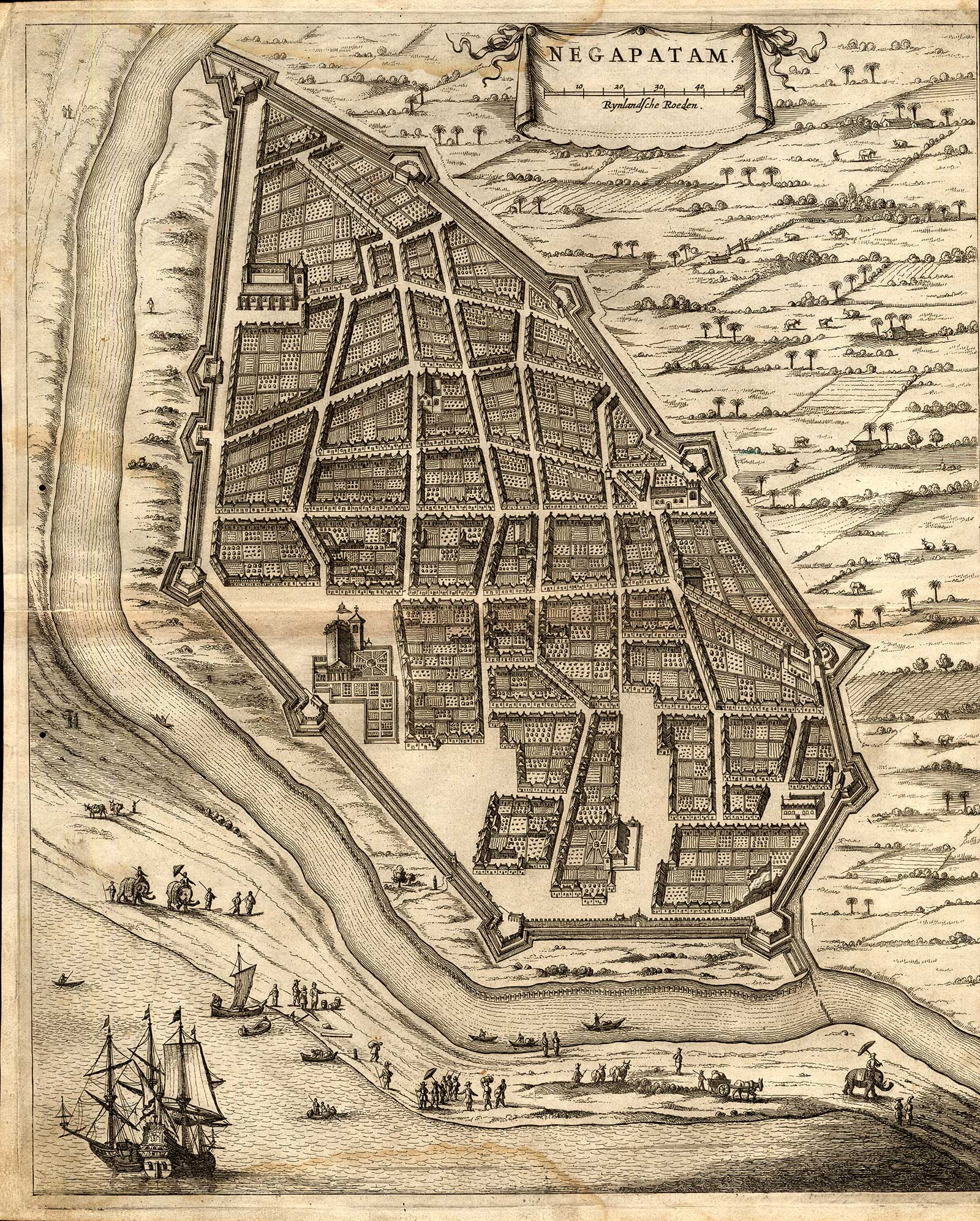


'Negapatnam opde kust van Choromandel', from 'Wouter
Schouten's Travels into the East Indies', 2nd ed., Amsterdam,
1708
Source: ebay, Aug. 2010



A Dutch fanam of the type minted at Negapatam, c.1657-1784
Source:
http://www.vcoins.com/ancient/coinindia/store/viewitem.asp?idProduct=241
(downloaded July 2007)
"DUTCH INDIA: Gold fanam, Negapatam type. Obverse Formalized figure of deity (Kali?) standing facing. Reverse Degenerate (geometric?) design. Date c. 1657-1784. Weight 0.34 gm. Diameter 6 mm."
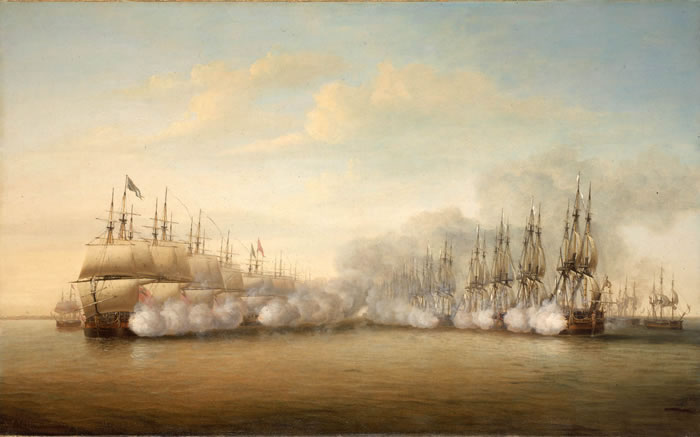

The Battle of Negapatam, 1782, between the French and the English
Source:
http://www.nmm.ac.uk/searchbin/searchs.pl?exhibit=it0516i&axis=1101400722&flash=true&dev=
(downloaded Dec. 2004)
"Battle of Negapatam, 6 July 1782. Artist: Dominic Serres, the
Elder. Date: 1786. Oil on canvas. 1117.6 x 1828.8 mm. National
Maritime Museum, London, Greenwich Hospital Collection. The French
were seeking to take control of the British-held port of Negapatam
on the eastern coast of India. There was no clear result but the
British managed to force a French retreat. The action was fought
with the two opposing fleets lined up in their squadrons firing at
each other. This line formation dominated sea warfare in the 18th
century."
== Indian Routes index == Indian Routes sitemap == Glossary == FWP's main page ==